1. What is a single phase AC motor?
A single-phase electric motor (also known as a single-phase electric motor) is a type of motor in which the stator winding consists of only 1 phase winding, and the main power supply is 1 phase wire and 1 cold wire (with an additional capacitor to phase deflection). However, if there is only 1 phase winding, then the motor will not be able to start the machine by itself, because the single phase magnetic field is the pulsed magnetic field.
In order for a single-phase motor to turn on, you can use many different methods. Asynchronous electric motor (symbol KDB) 1-phase 1-phase electric motor is often applied a lot in life, becoming an indispensable part in many different fields, such as: air compressor, winch, water pump, hand tools…

2. How to build a single phase electric motor?
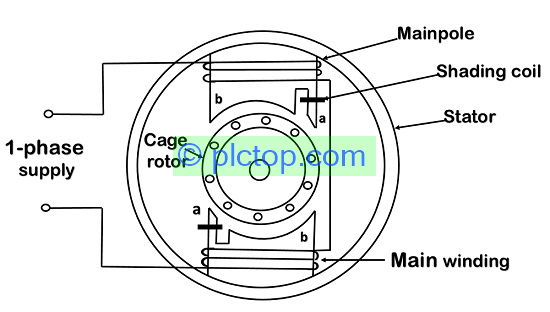
Static part: Also known as the stator, it consists of two main parts, the steel core and the winding part.
- Steel core: This is the magnetic conductive part of the machine, they have the shape of a dragon cylinder, the steel core is assembled from electrotechnical steel sheets with a thickness of 0.35 0.5mm, stamped in the shape of a towel, and the inside is slotted. so that the winding can be placed and covered with paint before closing.
- Winding: The stator winding is made of copper wire or aluminum wire (email wire type) and is placed in the inner grooves of the steel core. In addition to these two main parts, there are also auxiliary parts, which cover the main steel core, which is the case made of aluminum or cast iron, which can be used to hold the steel core below the base for the purpose of fastening. into the base of the machine, and at the same time, there are 2 caps made of the same material as the case, in the cover there is also a bearing (also known as silver) used to support the rotor’s axis of rotation.
The rotating part of a single-phase electric motor, also known as the rotor, includes:
- Steel core: Cylindrical form made of electrical engineering steel sheets, stamped into the shape of a disc and pressed tightly, with grooves on the surface to place guide bars or coils. The steel core is also fastened to the rotating shaft and placed on the 2 bearings of the stator unit.
- Winding: On the rotor, there are two types: squirrel cage rotor and winding rotor. The winding rotor has the windings that are wound like the stator, this type has the advantage of large torque, but the structure is very complicated and the cost is also relatively high.
- Squirrel cage rotor type: The construction of this type is very different from the winding of the stator. It is made by casting aluminum into the grooves of the rotor, thereby forming aluminum rods, and short-circuited at both ends and also casts more propellers to be able to cool the inside each time the rotor is rotated turn.
3. Working principle of single phase electric motor
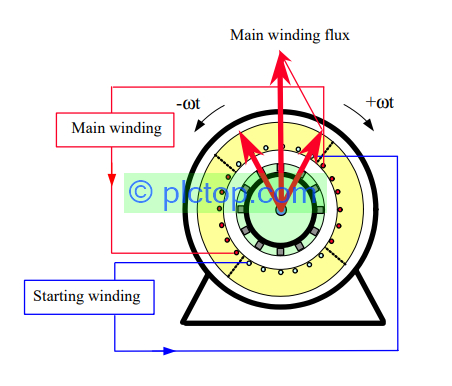
In order for a single phase electric motor to work, the stator of the motor needs to be supplied with an alternating current. Current flowing through the stator winding will create a magnetic field that rotates rapidly with speed: n = 60f/p (rpm). Where f is the frequency of the power supply, and p is the number of pole pairs of the stator winding.
During rotation, this magnetic field will continuously sweep across the rotor guides, causing an induced electromotive force. Since the rotor windings are closed circuit, this electromotive force will induce current in the rotor conductors. The current-carrying conductors are inside the magnetic field, so they will interact, creating an electromagnetic force that is applied to the conductors.
The combination of the above forces will create a rotational torque about the rotor’s axis, causing the rotor to rotate in the same direction as the magnetic track. When the motor is running, the speed of the rotor (n) is always less than the measured speed of the magnetic field (n1).
As a result, the rotors slow down, so they are always smaller than n1, hence the motor is also called asynchronous motor. The difference between the rotor speed and the magnetic field speed is also known as the slip coefficient, denoted by S, normally the measured slip is between 2% and 10%.
Application of single phase electric motor
Single phase 220V geared motor with capacity of 6W, 15W, 25W, 40W, 60W, 90W, 120W, 140Ww, 180W, 200W, 250W,… is widely applied in many fields, such as:
+ In industry: making conveyor belts, conveyor belts,…
+ In agriculture: making egg incubators, chicken feeding machines, etc.
+ In the machines to serve daily life: duck feather plucking machine, chicken feather plucking machine, duck roasting machine, chicken roasting machine…
+ In the fields used for advertising: display equipment, in bars, restaurants, hotels,
+ Depending on the field, people require products with good quality and reasonable prices.
+ Single-phase gear reducer motor 220V with capacity of 6W, 15W, 25W,…







