1. What is Contactor?
Contactor, also known as Magnetic Starter, is a low-voltage electrical device that makes regular switching of electrodynamic circuits. When you learn this device, you will learn in the subject of Electrical Instruments, QThang synthesizes to share with you the basic and practical knowledge you need to know and remember for your work.

2. Application of Contactor
For simplicity, the contactor is used as an intermediate switching device. You can see the picture below to get a clear understanding of how the contactor works.
In fact, control the contactor through the intermediate relay to ensure the safety and durability of the PLC.
3. Structure and working principle of Contactor
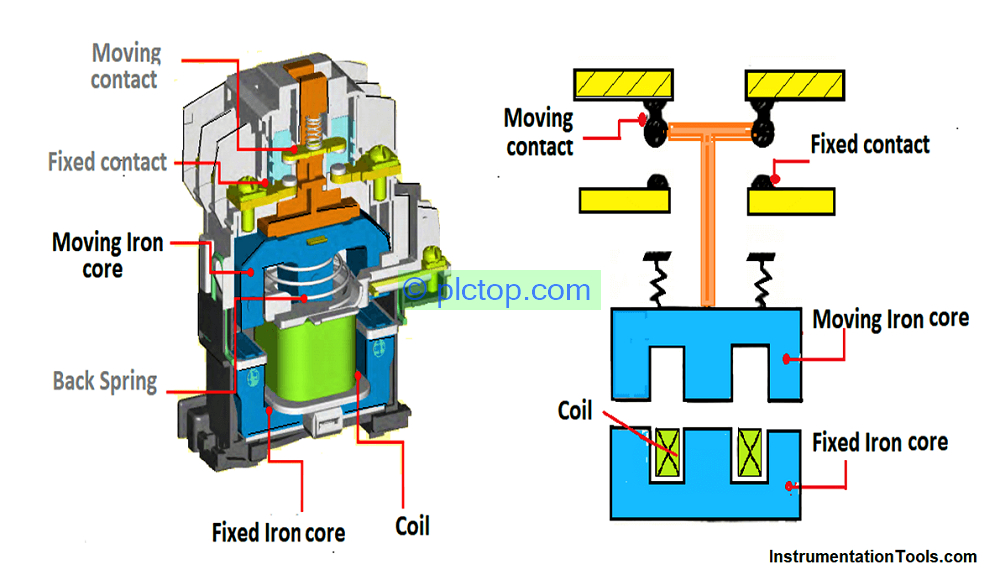
Contactor consists of 3 main parts:
- Electromagnet
- Dynamic contact
- Static contact
There is also an arc extinguishing system because when the contacts are switched off, an arc will be generated that will gradually burn the contacts
Working principle of contactor:
+ When power is applied to the two ends of the coil wound on the previously fixed magnetic core, the generated magnetic force will attract the movable magnetic core and form a closed magnetic circuit (at this time the magnetic force will be greater than the reaction of the spring). ). Contactor starts active state.
Basic parameter of contactor:
+ Rated current: is the current flowing through the main contact of the contactor
+ Rated voltage: is the voltage applied to the main contact of the contactor
+ Rated voltage of the suction coil: is the input voltage that makes the contactor work
4. Classification of Contactors
- According to the transmission principle: electromagnetic contactor, hydraulic type, pneumatic type, …
- According to current form: AC contactor and DC contactor
- According to structure: people divide contactor based on installation location
- According to rated current: 9A, 12A, 40A, 100A,… or more
- By number of poles: 1-phase, 2-phase, 3-phase, 4-phase contactor, the most common is 3-phase contactor
- By voltage level: Medium voltage contactor, low voltage contactor
- According to the suction coil voltage: AC 220V or 380V suction coil, DC 24V or 48V suction coil…
5. How to calculate and select Contactor
First, you need to choose according to the voltage parameter used to control the contactor. Commonly used are: 24VDC, 220V, 380V, 24VAC, 110V.
Calculating Contactor by Current
Selecting the correct contactor protects the contactor from damage when used with inductive loads with high starting currents such as motors. Resistive loads such as heating rods usually use less contactors and use SSRs. Contactor is mainly used for motor load.
Select contactor for 3 phase motor
P= √3UIcosφ ⇒ I = P/(√3Ucosφ)
- I is the motor current used (rated current)
- P is the motor power (W), this parameter is mounted on the motor housing, if the motor says 1HP = 0.75KW = 750W. Example: 7.5HP = (0.75*7.5)kW = 5.6kW=5600W
- U is the voltage applied to the motor
- Cosφ is the power factor
For example: 380V 3-phase electric motor with a capacity of 2.2KW, Cosφ = 0.8
>>> I = P/(√3*380*0.8) ≈ P/526.5 = 2200/526.5 = 4.2A
Select contactor for single phase motor
P= UIcosφ ⇒ I = P/(Ucosφ)
- I is the motor current used (rated current).
- P is the motor power, in watts (W).
- U is the usable voltage.
- Cosφ is the power factor.
For example: 220VAC motor, power 2.2KW, cosφ = 0.8
>>> I = P/(Ucosφ) = 2200(220*0.8) = 12A








